We document that a centralization decision-making culture of global banks affects the transmission of shocks from parent banks to their subsidiaries. Using a novel measure of integration culture of multinational banking conglomerates based on the prevalence of a language of power and authority in financial reports, we find that subsidiaries of banks with a relatively more autocratic integration culture cut …
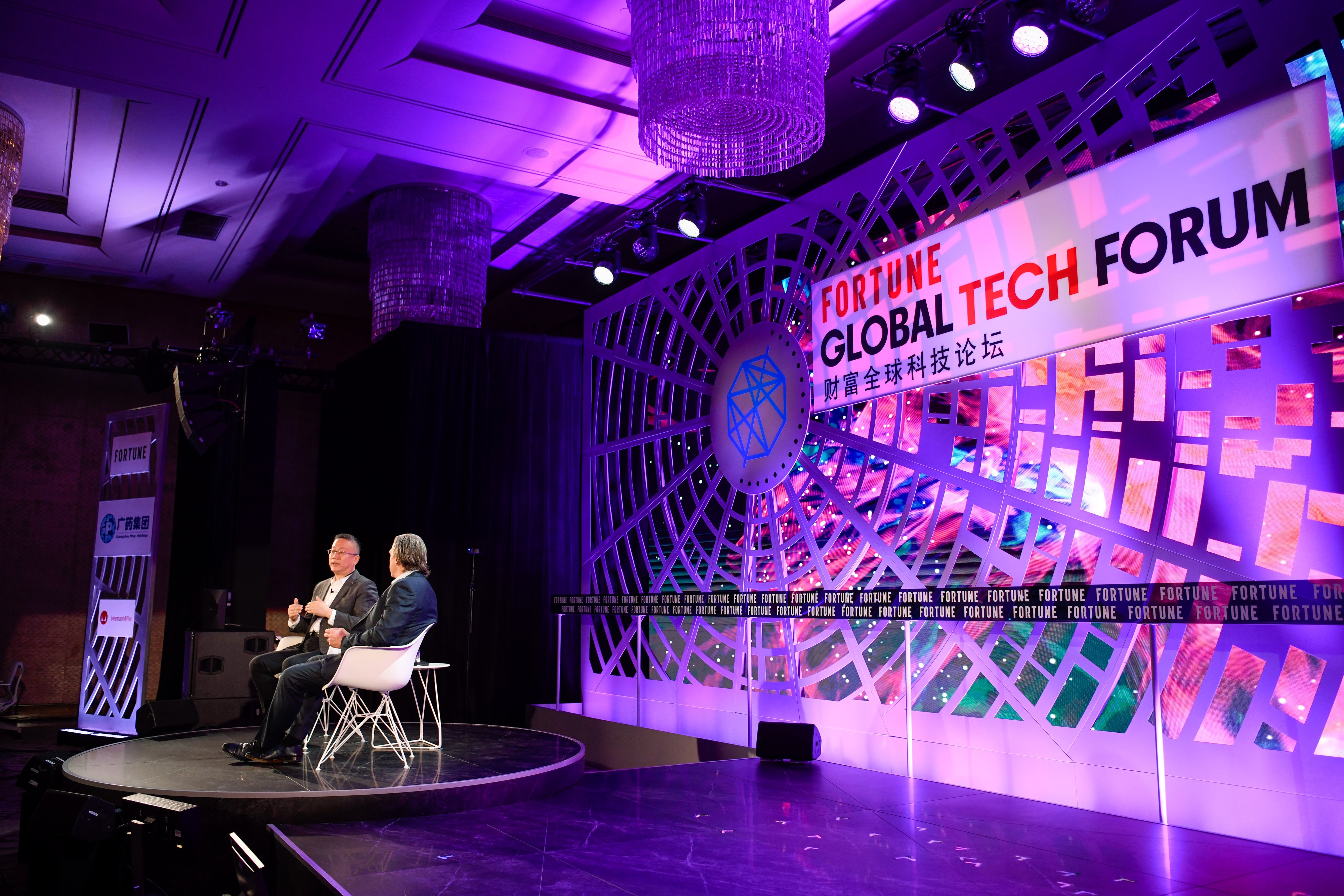
The Fortune Global Technology Forum, Day One
Good morning. The Fortune Global Technology Forum got underway this morning in Guangzhou, China. Some excerpts from Fortune’s coverage: “I think innovation means you are willing to do things that others don’t dare.” —Fu Sheng, founder and CEO, Cheetah Mobile. “4G is like driving on the high-speed interstate highway. 2G is like driving on a country road. But 5G is like flying an …
Central banks push green finance as global warming losses rise to $160 b
With insurers shouldering a record $160 billion in climate-related losses from last year alone, a group, including 30 central banks, called for measures to spur green finance and better assessment of the risks from higher global temperatures. The move, led by the Bank of France, Bank of England and People’s Bank of China, draws the group deeper into a controversial …
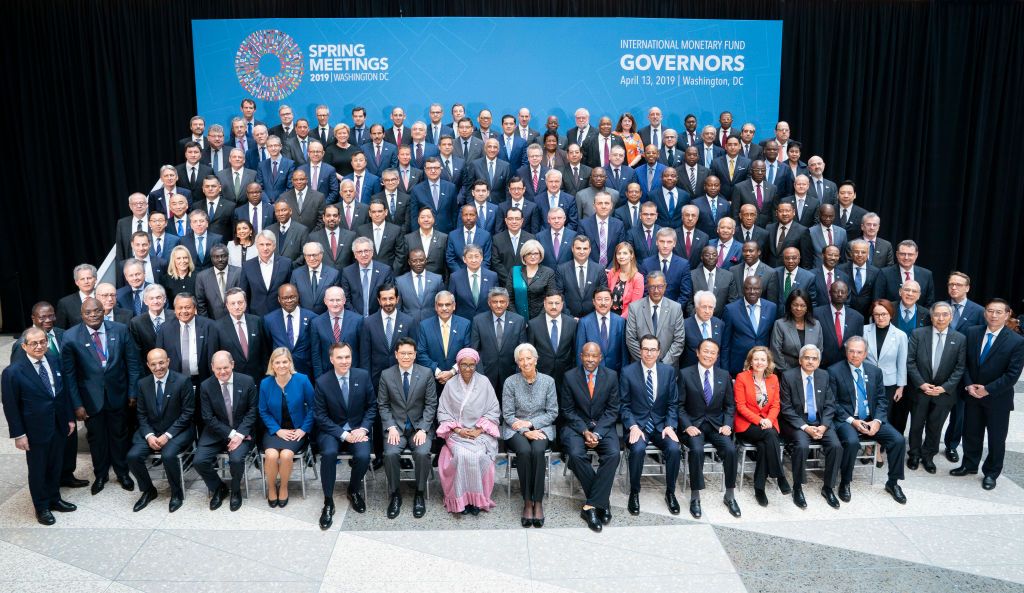
Global Finance Officials Pledge to Lift World Economy Out of Slowdown
(WASHINGTON) — Global finance officials are pledging closer cooperation in efforts to lift the world economy out its current slowdown, but tensions persist on a number of fronts between the United States and other nations over trade and other issues. Officials wrapped up the spring meetings of the 189-nation International Monetary Fund and the World Bank on Saturday, expressing hope …
Hold Shriram Transport Finance Company, target Rs 1,181: Emkay Global Financial Services
View of the brokerage- MHCV slowdown resulting in slower disbursements: The domestic MHCVs are showing tepid demand due to high base effect, rural distress, changes in axle norms, leading to surplus capacity and slowdown in real estate. Although the implementation of BSVI emission norms may drive some pre-buying for CVs, the used CV segment is at a downturn as driver-owner is …
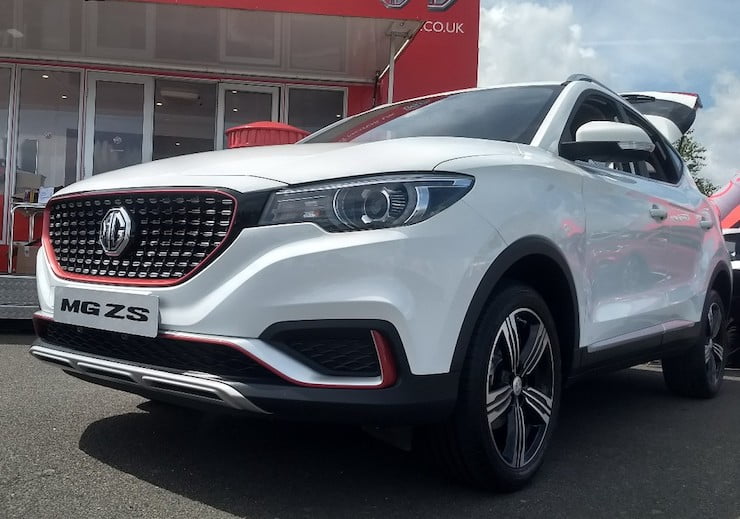
First impressions of MG ZS SUV – Ford EcoSport’s global rival
During our recent visit to the Silverstone race track for the #MGLive2018 event, we managed to get our hands on the much awaited and highly speculative (for India) MG ZS SUV. The quick drive lasted about ten minutes as we drove around the outer periphery of the racing circuit but later, I had more than ample time to spend with …
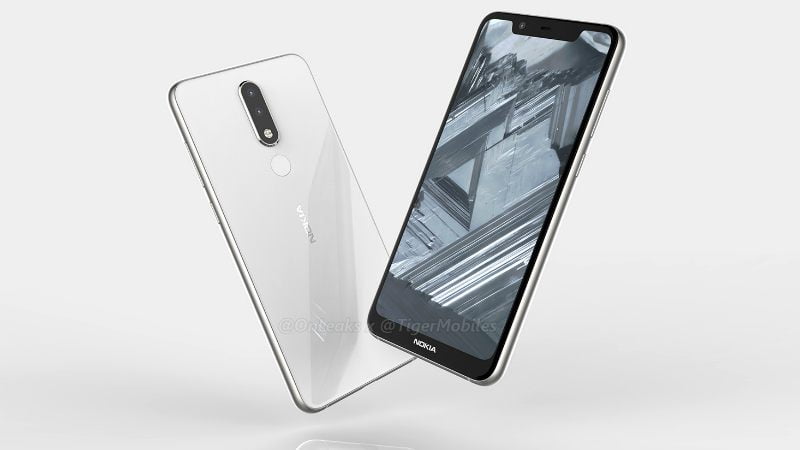
Nokia 5.1 Plus Renders Surfaced, Nokia X6 Global Variant Said to Receive Taiwan’s NCC Certification
HIGHLIGHTS Nokia 5.1 Plus renders surfaced The renders show a notch design and a dual rear camera setup Nokia X6 global variant has also received a certification in Taiwan While HMD Global is seemingly busy in making the newly launched Nokia 2 (2018), Nokia 3 (2018), and Nokia 5 (2018) available across the worldwide markets, renders highlighting the Nokia 5.1 Plus have surfaced online. The renders …
Nokia 2 and Other HMD Global Phones Will Not Support Project Treble
HIGHLIGHTS Project Treble is not coming to current Nokia family Smartphones don’t have a separate Vendor implementation Absence of Project Treble support will have “no end-user impact” HMD Global has confirmed that Google’s Project Treble will not be a part of any currently available Nokia phones, including the most affordable Nokia 2 and the flagship Nokia 8. The project, which was announced back in May, …
Xiaomi Seeks to Reignite Global Push With Spain Launch
HIGHLIGHTS Xiaomi will sell a range of products in its first Western Europe market It will offer the Xiaomi Mi A1 smartphone in Spain Scooters, air purifiers, and coffee makers will also be sold Chinese smartphone maker Xiaomi launched sales in Spain on Tuesday, its first foray into Western Europe as it revs up a stalled global push into other developed markets …
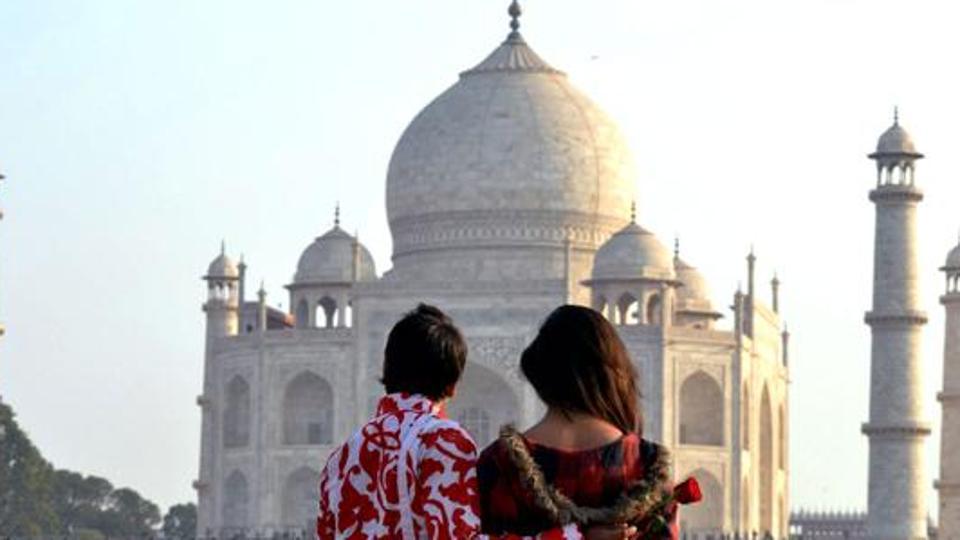
Travellers’ choice: Taj Mahal only Indian monument to figure in top 10 global landmarks
Taj Mahal, the magnificent monument of love, has made it to the top 10 landmarks in the world by securing fifth position in the list. One of the most iconic wonders in the world, the Agra- based imposing white marble structure, a tourist delight, is the only Indian monument to figure in the world’s top 10 Travellers’ Choice awards for …